Researchers discovered a new variant of Muhstik IoT Botnet that targets the vulnerable Linux-based Tomato routers to perform DDOS Attack, launch cryptocurrency mining to earn profits, and harvest the new IoT devices.
Tomato is an open-source Linux-based, non-proprietary firmware, alternative firmware for routers and is commonly installed by multiple router vendors and also installed manually by end-users.
The new variant of Muhstik botnet comes with the scanner to harvest the vulnerable routers for the first time by web authentication brute-forcing attack.
Based on the Shodan results, researchers found more than 4,600 Tomato routers exposed on the Internet and vulnerable to Muhstik Botnet attack.

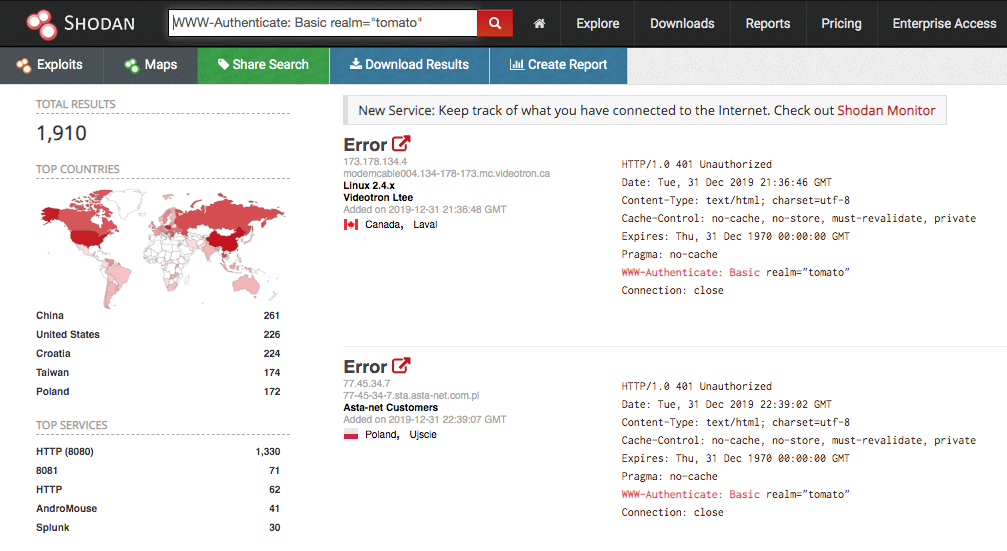
This total number of infected devices derived by including the number of TomatoUSB devices, that are used as a NAS server by combining the Tomato router and a USB drive.
Muhstik Botnet is active since 2018, as well as it contains the self-propagating capability to infect Linux servers as well as IoT devices, and it used multiple vulnerabilities exploit to infect the Linux systems.
Muhstik Botnet Scanner
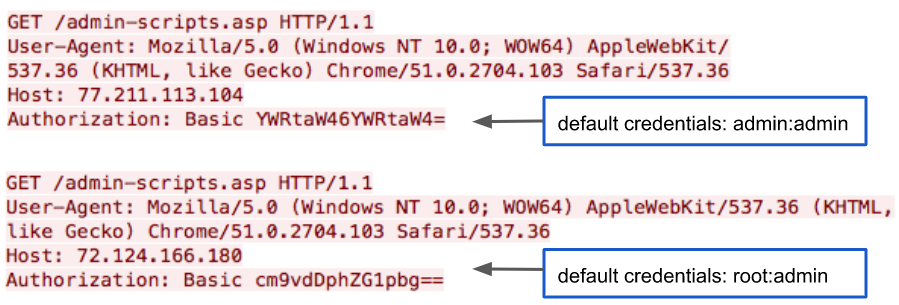
Muhstik Botnet Scanner initially scans Tomato routers on TCP port 8080 and attempt to bypass the admin web-based authentication by initiating brute forcing attack based on default credentials.
Muhstik employed some other scanning module, in which, the first module scanner is scanning to identify WordPress installed on a server by sending a request to HTTP port 80/tcp or 8080/tcp.
“The second module scanning the to identify Webuzo solutions installed on a server by sending sends a GET request to port 2004/tcp, which is Webuzo’s default port for administration.”
3rd module targeting the WebLogic server versions 10.3.6.0 and 12.1.3.0 and try to exploit the CVE-2019-2725 and the attackers send the exploit to port 7001/tcp since its WebLogic Server’s default port.
Muhstik Botnet Execution Flaw
Muhstik Botnet scanner agent initially scanning the IoT devices and report to the server about the vulnerable server and IoT devices.
A loader server starts exploiting the vulnerable IoT devices and joins it in a botnet network.
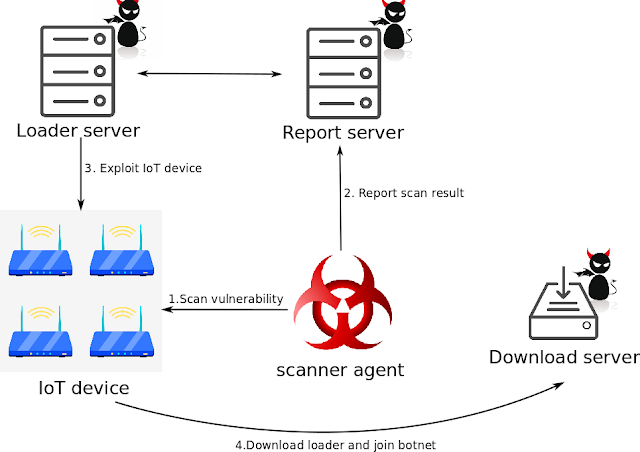
According to PaloAlto network research ” Once a device is compromised, it will send a connect command to an IRC server. The connect command includes a nickname (NICK) for the device in order to join the channel”
“The new Muhstik botnet variant demonstrates that IoT botnet keeps expanding the botnet size by adding new scanners and exploits to harvest new IoT devices.”
Its a sign of IoT botnet evaluation and increasingly compromising IoT devices installed with the open-source firmware due to the lack of security and failed to apply the firmware updates.
Also Read: Dutch Police Seized Bulletproof Hosting Used to Control DDoS Botnets





